High Availability for Search
Search delivers key high availability features such as zero downtime administration and maintenance, built-in optional data redundancy, and manual failover.
Factors that increase system uptime and availability include:
-
Number of replicas
-
Number of racks or availability zones
-
Index alias
High Availability Indexes
High availability indexes help users prevent downtime caused by unplanned incidents and enhance the overall system availability. It is achieved through Replica and Failover mechanisms with Search Service.
Replica for the index is not automatically enabled. The user must explicitly configure the required number of replicas for the index partitions according to their availability needs during the index creation step. Refer Index Replicas to the index replica section during index creation. They could also update the replica count without rebuilding the primary partitions or live traffic for an existing index.
Server Groups/Rack zone awareness
Server Group Awareness provides enhanced availability for the Search Service. Specifically, it protects a cluster from large-scale infrastructure failures through the definition of server groups. Each server group is created by an appropriately authorized administrator and specified to contain a subset of the nodes within a Couchbase Cluster. Server groups should be defined in accordance with the physical distribution of cluster nodes. For example, a server group should only include the nodes that are in a single server rack, or in the case of cloud deployments, a single availability zone.
Following the group definition and rebalance, the primary partitions for any Search indexes are located on one group, while the corresponding replicas are located on another server group and this makes the Group recovery possible. Whenever an entire group/rack goes offline making the primary index partitions inaccessible, the replica index partitions that remain available on another group can be failed over and promoted to primary/active status. Such failure protection is optimal when the groups are assigned equal numbers of nodes, and index partition replicas are thereby distributed such that none ever occupies the same group along with its associated primary partitions.
Search service would place the index replicas on separate server groups as long as there is enough number of server groups (with Search service) equal to the number of replicas available in the cluster. If not, then it would end up positioning multiple replicas on the same server group/rack.
| Optimum distribution - when the number of index replicas created for a given index is at least one less than the total number of groups for the cluster, and each group contains sufficient nodes running the Search Service, automatic distribution ensures that each index and index replica resides on its own exclusive group. This configuration gives the High Availability for the Search service. |
By contrast, when groups are not assigned equal numbers of nodes, rebalance can only produce the best effort redistribution of replicas: this may result in one or more replica index partitions each occupying the same group as their associated primary counterparts; meaning that index partition data may be lost if such a group becomes unavailable.
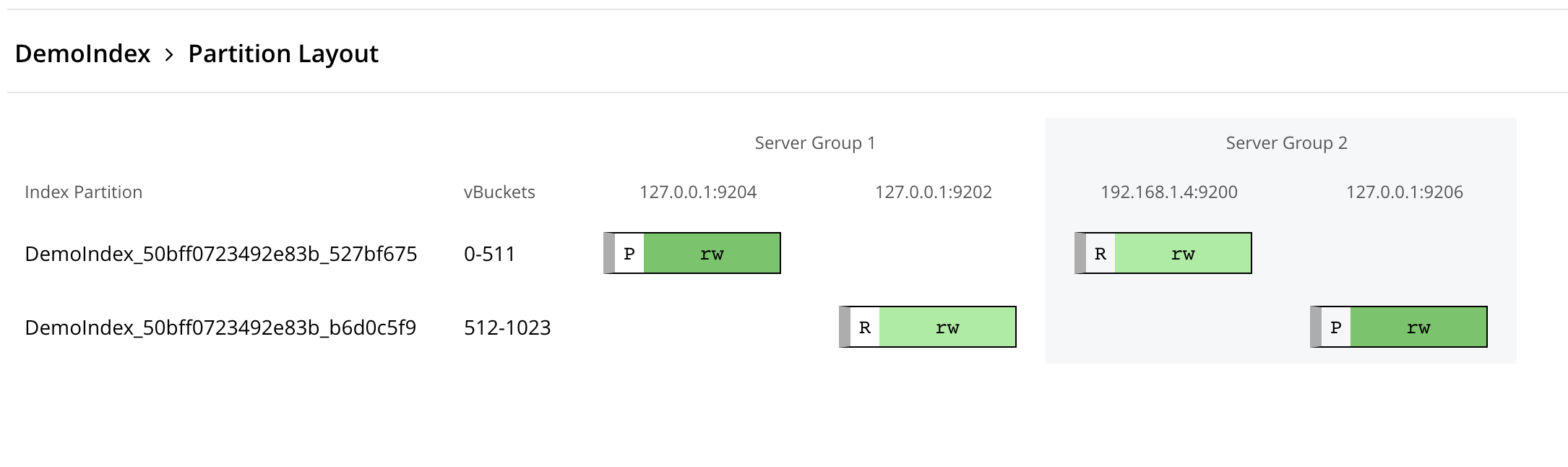
The above picture shows a sample allocation when we have a single index with 2 partitions and 1 replica enabled in a cluster with 2 Server Groups.
And we can see, here every rack/server group is hosting the complete set of primary and replica partitions to provide the High Availability to the Search Service.
As of Couchbase Server 7.1, the Search service doesn’t offer auto-failover capability upon node/rack down situations. In the case of server groups/rack down scenarios, the administrator has to explicitly failover the nodes to ensure the seamless service for Search.
Zero Downtime Index Upgrades
Users can update/recreate/rebuild the indexes without interfering with the live systems by leveraging the index-alias feature. The index aliases permit indirection in the index naming, whereby applications refer to an alias-name that never changes, leaving administrators free to change the identity of the real index pointed to by the alias. This may be particularly useful when an index needs to be updated: to avoid downtime, while the current index remains in service, a clone of the current index can be created, modified, and tested. Then, when the clone is ready, the existing alias can be retargeted so that the clone becomes the current index; and the (now) previous index can be removed.