General
General settings allow configuration of cluster name, memory quotas, storage modes, and node availability for the cluster; and of advanced settings for the Index and Query Services.
Examples on This Page
Full and Cluster Administrators can configure general settings by means of Couchbase Web Console, the CLI, or the REST API.
Configure General Settings with the UI
The appearance of the General screen is as follows:
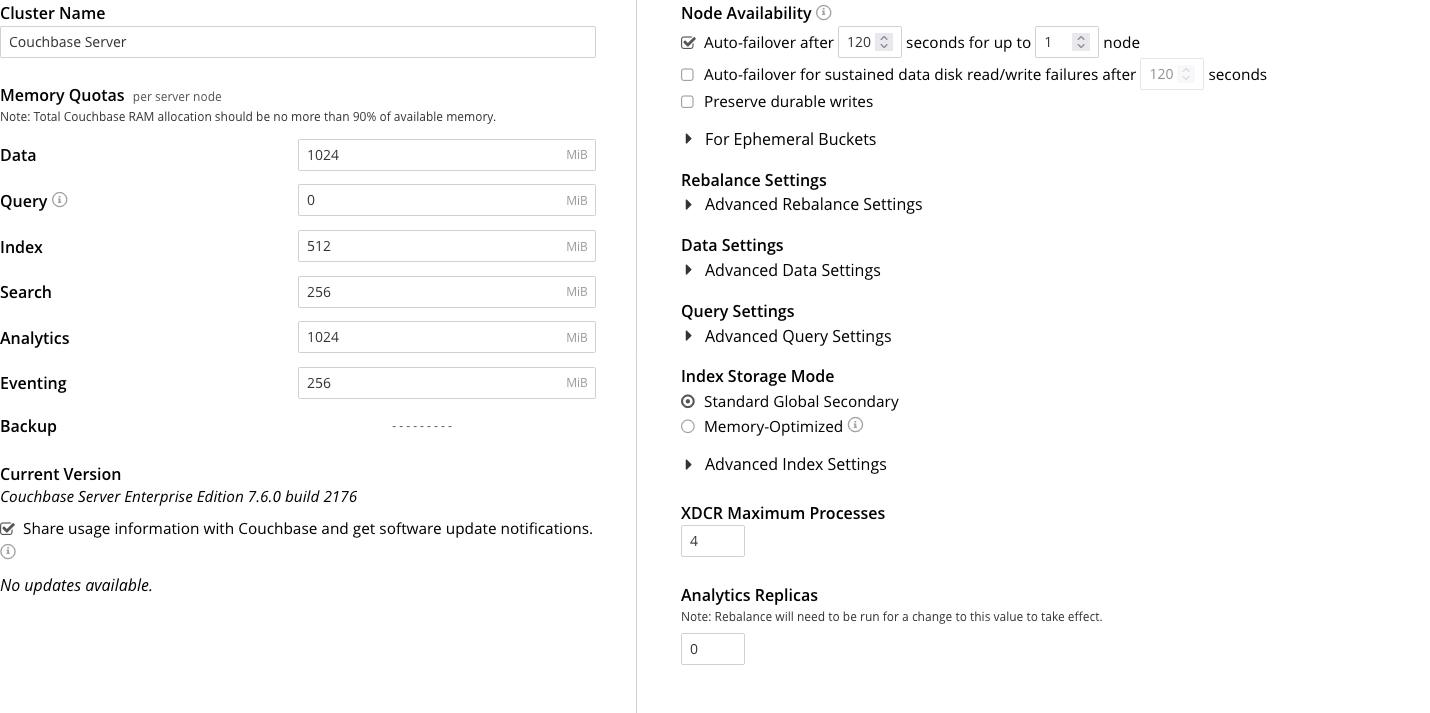
The panels and their UI elements are described below.
Cluster Name
The Cluster Name is the name that was given during initial setup. This name can be changed at any time. The interactive field appears as follows:

Memory Quotas
The amount of memory available to each service, on every node. The combination of assigned values is not permitted to exceed the total memory available on the most memory-constrained node.
The panel appears as follows:

The displayed, configurable options are:
-
Data. The memory allocation for the Data Service, per node. The minimum allocation must be equal to or greater than the sum of all per bucket memory-allocations on the node.
-
Query. The soft memory limit for every Query node in the cluster. The garbage collector tries to keep below this target. It is not a hard, absolute limit, and memory usage may exceed this value. When set to
0(the default), there is no soft memory limit. -
Index. The buffer cache size for the Index Service. The specified amount of memory is pre-allocated as soon as the Index Service starts up. It is then shared with all indexes created on the node. The total memory-usage of the indexer process will be the buffer cache size plus the size of various internal data structures and queues.
-
Search. The memory allocation for the Search Service, per node.
-
Analytics. The memory allocation for the Analytics Service, per node.
-
Eventing. The memory allocation for the Eventing Service, per node.
Note that the Backup Service does not require memory-allocation.
Current Version
This panel displays the current version of Couchbase Server, and can be used to indicate whether updates are available. It appears as follows:

The Share usage information with Couchbase and get software update notifications checkbox is checked by default: this means that Couchbase Web Console will display adjacent notifications whenever a new version of Couchbase Server is available. If the checkbox is unchecked, notifications are not provided.
Additionally, if the checkbox is checked, Couchbase Web Console communicates with Couchbase Server to ascertain the following information, which is then transmitted to Couchbase:
-
The server-version of the current installation.
-
Information about data-size and performance.
-
The cluster-configuration, including which services are deployed.
Note that data is transmitted to Couchbase from the browser accessing the web console, not from the cluster itself. The update-notification process works anonymously: data cannot be tracked. No identifiable information (such as bucket names, bucket data, design-document names, or hostnames) is transmitted.
Node Availability
The options in the Node Availability panel control whether and how Automatic Failover is applied. For detailed information on policy and constraints, see Automatic Failover.
The panel appears as follows:
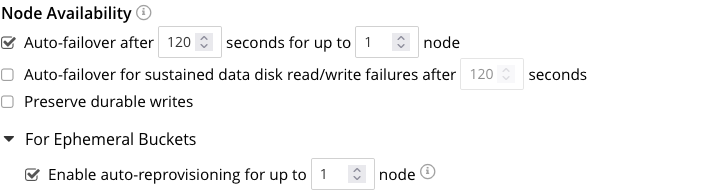
The following checkboxes are provided:
-
Auto-failover after x seconds for up to y node: After the timeout period set here as x seconds has elapsed, an unresponsive or malfunctioning node is failed over, provided that the limit on actionable events set here as y (with the default value of 1) has not yet been reached. Data replicas are promoted to active on other nodes, as appropriate. This feature can only be used when three or more nodes are present in the cluster. The number of seconds to elapse is configurable: the default is 120; the minimum permitted is 5; the maximum 3600. This option is selected by default.
-
Auto-failover for sustained data disk read/write failures after z seconds: After the timeout period set here as z seconds has elapsed, a node is failed over if it has experienced sustained data disk read/write failures. The timeout period is configurable: the default length is 120 seconds; the minimum permitted is 5; the maximum 3600. This checkbox can only be checked if Auto-failover after x seconds for up to y node has also been checked. This option is unchecked by default.
-
Preserve durable writes: If this checkbox is checked, a node is not failed over if this might result in the loss of durably written data. The default is that the checkbox is unchecked. For information, see Preserving Durable Writes.
The Node Availability panel also contains a For Ephemeral Buckets option. When opened, this provides an Enable auto-reprovisioning checkbox, with a configurable number of nodes. Checking this ensures that if a node containing active Ephemeral buckets becomes unavailable, its replicas on the specified number of other nodes are promoted to active status as appropriate, to avoid data-loss. Note, however, that this may leave the cluster in an unbalanced state, requiring a rebalance.
Auto-Failover and Durability
Couchbase Server provides durability, which ensures the greatest likelihood of data-writes surviving unexpected anomalies, such as node-outages. The auto-failover maximum should be established to support guarantees of durability. See Durability, for information.
Rebalance Settings
Rebalance redistributes data, indexes, event processing, and query processing among available nodes. For an overview, see Rebalance. Fully open, the panel appears as follows:
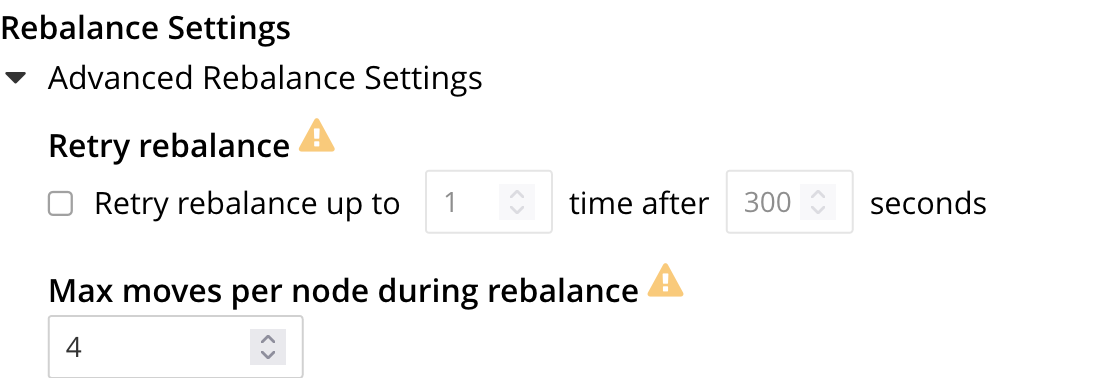
The Retry rebalance option allows rebalance to be retried, in cases where it has failed. Check the checkbox, to enable. The specifiable, maximum number of retries must be in the range of 1 to 3, inclusive. The specifiable, maximum number of seconds must be in the range of 5 to 3600, inclusive.
Note that this option should not be enabled if the cluster is managed by Couchbase Autonomous Operator, or if custom scripts are already being used to trigger rebalance. Note also that no administrative tasks should be attempted when rebalance-retries are pending. However, pending rebalance-retries can be cancelled: see Automated Rebalance-Failure Handling, for information.
The Max moves per node during rebalance option establishes the maximum number of concurrent vBucket moves permitted on every individual node.
The minimum value for the parameter is 1, the maximum 64, the default 4.
For information, see Limiting Concurrent vBucket Moves.
Data Settings
The settings in this area control the numbers of threads that are allocated per node by Couchbase Server to the reading and writing of data, respectively. The maximum thread-allocation to each is 64, the minimum 4.
A high thread-allocation may improve performance on systems whose hardware-resources are commensurately supportive (for example, where the number of CPU cores is high). In particular, a high number of writer threads on such systems may significantly optimize the performance of durable writes: see Durability, for information.
Note, however, that a high thread-allocation might impair some aspects of system-performance on less appropriately resourced nodes. Consequently, changes to the default thread-allocation should not be made to production systems without prior testing.
Left-clicking on the Advanced Data Settings tab displays radio buttons for Reader Thread Settings and Writer Thread Settings:
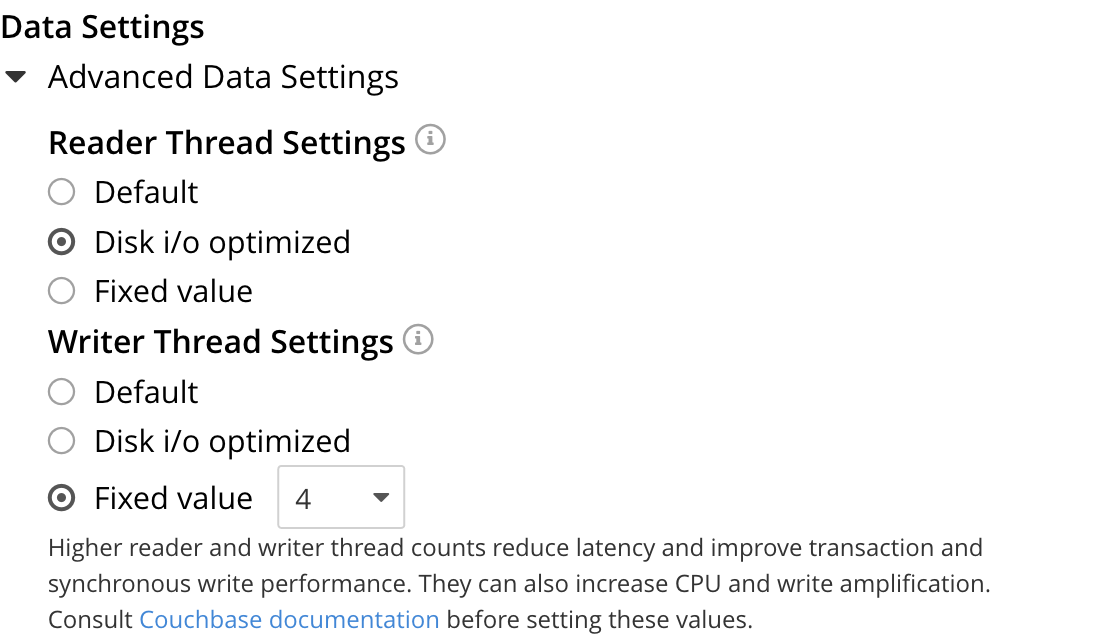
Each group has the same, three radio buttons, which are as follows:
-
Default. The number of threads allocated is set to a balanced value which is reasonable for most workloads.
-
Disk i/o optimized. The number of threads allocated is equal to the number of CPU cores for the node.
In order to get maximum performance from Magma for disk-oriented workloads, it is recommended to set the Writer Threads to 'Disk i/o optimized'. This setting will ensure there are enough threads to sustain high write rates.
To Learn more about the Magma Storage Engine, see Storage Engines — Magma Storage Engine. -
Fixed value. The number of threads allocated is equal to the value selected from the pull-down menu.
A good rule of thumb is to set each of readers and writers equal to the queue depth of the underlying IO subsystem (i.e. readers = queue_depth and writers = queue_depth).
However, for best performance it is recommended to benchmark with different settings and pick the one that best meets the throughput and latency requirements in your environment.
Query Settings
Left-clicking on Advanced Query Settings displays interactive fields with which you can configure the Query Service. The top section of the panel appears as follows:
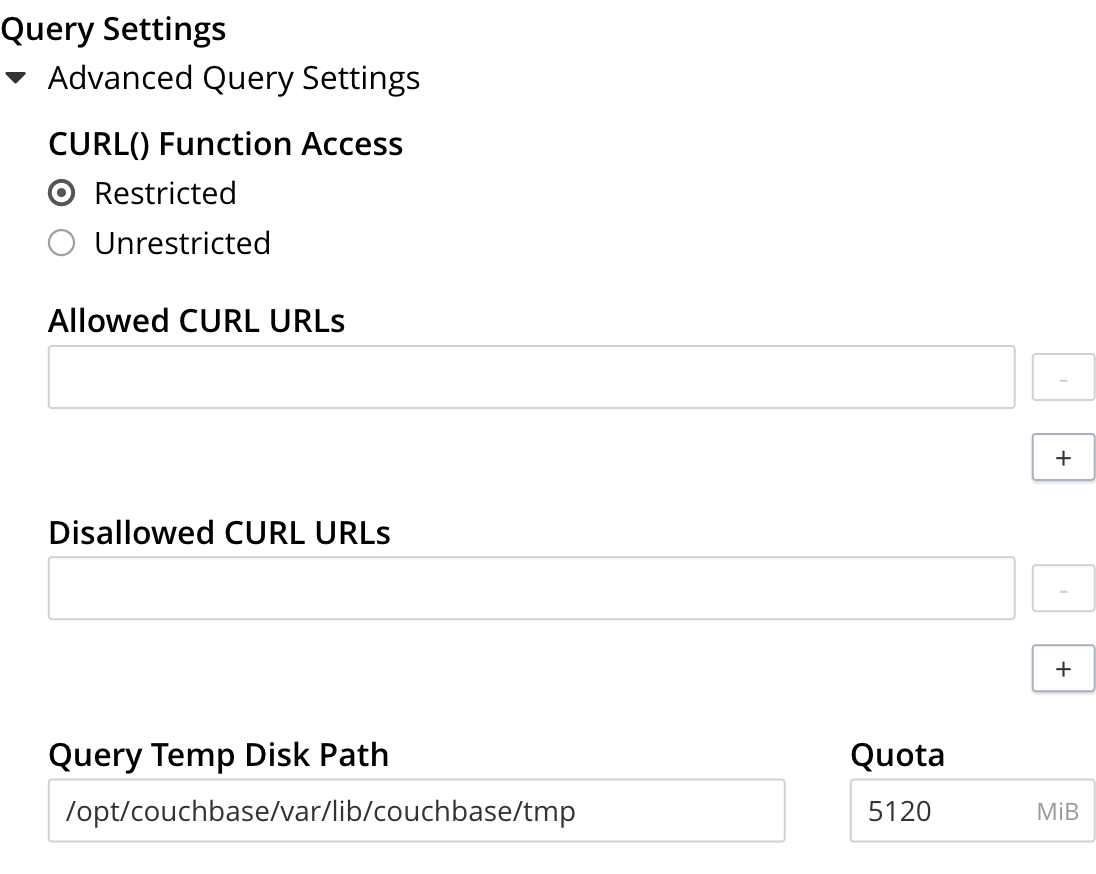
Under CURL() Function Access, specify either Unrestricted or Restricted, to determine which URLs the CURL() function can access.
-
If you specify Unrestricted (the default), the CURL() function can access all URLs.
-
If you specify Restricted, the UI expands, to display configurable fields into which you can enter the allowed and disallowed URLs.
When a query has an extremely large corresponding index scan, the indexer buffers the results into a temporary directory. Since this method may cause high I/O and works differently on Windows, you can configure backfill settings for the SQL++ engine and its embedded GSI client.
-
The Query Temp Disk Path field enables you to specify the path to which the indexer writes temporary backfill files, to store any transient data during query processing. The specified path must already exist. Only absolute paths are allowed. The default path is
var/lib/couchbase/tmpwithin the Couchbase Server installation directory. -
The Quota field enables you to specify the maximum size of temporary backfill files, in megabytes. Setting the size to
0disables backfill. Setting the size to-1means the size is unlimited. The maximum size is limited only by the available disk space.
Additional Query settings are provided in the lower section of the panel:
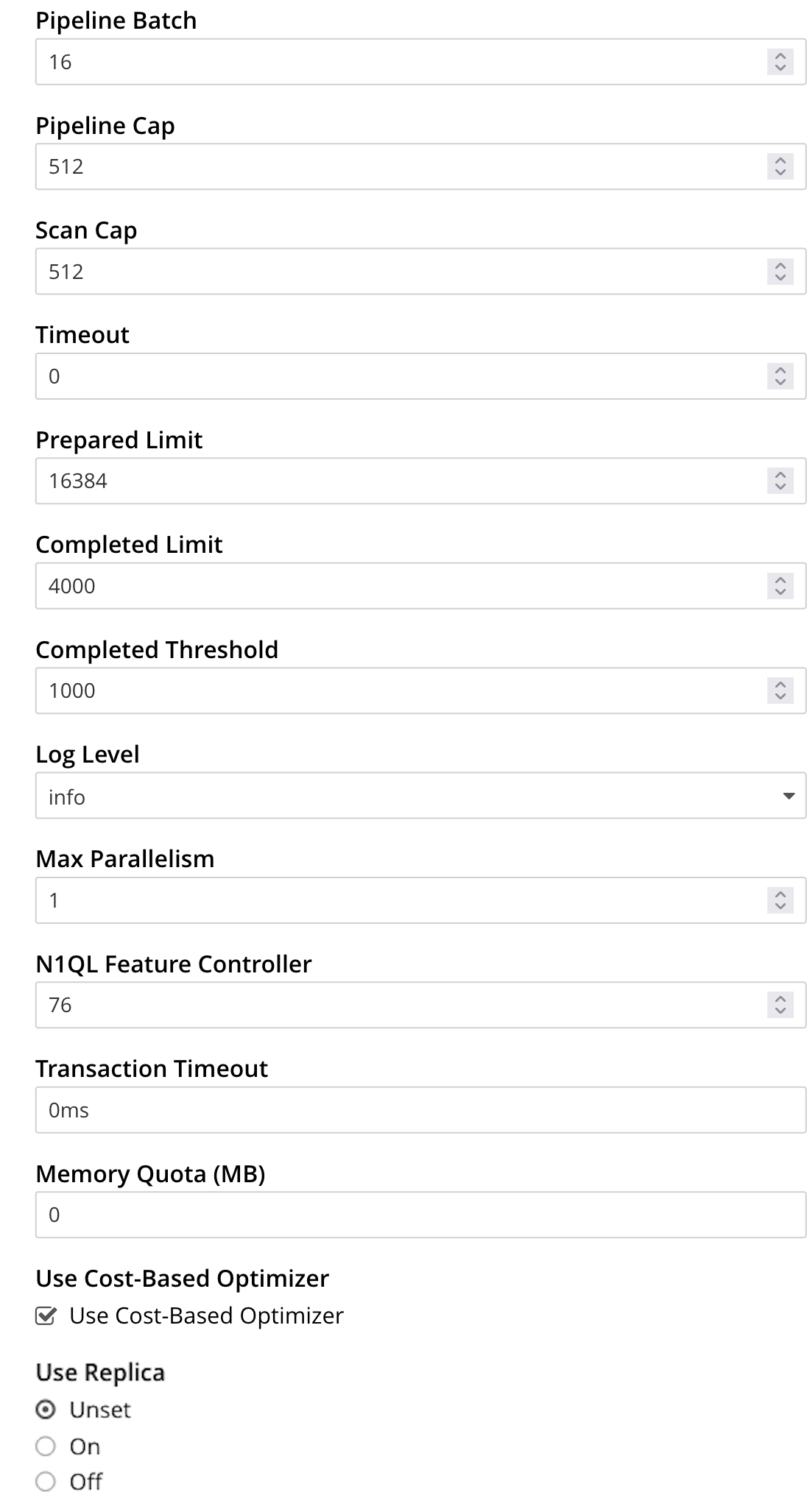
-
Pipeline Batch: The number of items that can be batched for fetches from the Data Service.
-
Pipeline Cap: The maximum number of items that can be buffered in a fetch.
-
Scan Cap: The maximum buffered channel size between the indexer client and the Query Service, for index scans.
-
Timeout: The maximum time to spend on a request before timing out.
-
Prepared Limit: The maximum number of prepared statements to be held in the cache.
-
Completed Limit: The number of requests to be logged in the completed requests catalog.
-
Completed Threshold: The completed-query duration (in milliseconds) beyond which the query is logged in the completed requests catalog.
-
Log Level: The log level used in the logger.
-
Max Parallelism: The maximum number of index partitions for parallel aggregation-computing.
-
N1QL Feature Controller: Enables or disables features in the Query engine.
Do not change the N1QL Feature Controller setting without guidance from technical support. -
Transaction Timeout: The number of milliseconds to elapse before a transaction times out.
-
Memory Quota: The amount of memory, in megabytes, allocated to the processing of a query.
-
Use Cost-Based Optimizer: when checked (as it is by default), specifies that the cost-based optimizer is used for queries: when the checkbox is unchecked, the optimizer is not used.
-
Use Replica: specifies whether a query can fetch data from a replica vBucket if active vBuckets are inaccessible. The possible values are:
-
Unset — read from replica is enabled or disabled at request level.
-
On — read from replica is enabled for all queries, but can be disabled at request level.
-
Off — read from replica is disabled for all queries and cannot be overridden at request level.
Do not enable read from replica when you require consistent results. Only SELECT queries that are not within a transaction can read from replica.
Note that KV range scans cannot currently be started on a replica vBucket. If a query uses sequential scan and a data node becomes unavailable, the query might return an error, even if read from replica is enabled for the request.
-
For additional details on all the Query settings in the lower section of the panel, refer to Configure Queries.
Index Storage Mode
This panel provides radio buttons that set the storage mode for indexes and some additional index settings:
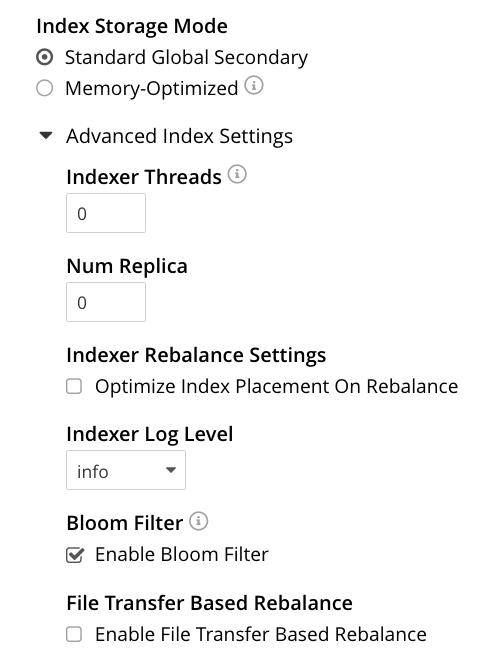
The index storage mode options are Memory Optimized Index Storage, and Standard Index Storage.
The settings under Advanced Settings for indexes are:
-
Indexer Threads: Sets the number of threads the Index Service uses. You can increase the number of threads dedicated to the Index Service on multi-core machines. The default value of 0 has the Index Service use one thread per core on the node.
-
Num Replica: Sets the default number of index replicas the Index Service creates for new indexes. Defaults to 0 (no replicas). See Index Replication.
-
Indexer Rebalance Settings: When cleared, Optimize Index Placement On Rebalance has Couchbase Server only redistribute indexes during a rebalance when the nodes containing them are leaving the cluster. When selected, Couchbase Server redistribute indexes among the Index Service nodes during a rebalance to optimize performance. See Index Redistribution.
-
Indexer Log Level: Sets the logging level. The options are:
Silent,Fatal,Error,Warn,Info,Verbose,Timing,Debug, andTrace. The default isInfo. -
Bloom Filter: The default cleared setting for Enable Bloom Filter turns off Bloom filters for memory management. When selected, Enable Bloom Filter enables Bloom filters. See Per Page Bloom Filters.
7.2.1+ From release 7.2.1 onward, Bloom filters for plasma back indexes will be enabled by default. During an upgrade, mixed mode clusters with nodes that support bloom filters will enable it for back indexes, even if they was disabled in the past. Users must explicitly disable it again after a cluster setup, or a new node is added.
Once bloom filters are disabled in mixed mode, adding a new 7.2.1+ node will not re-enable them.
-
File Transfer Based Rebalance: Controls whether Couchbase Server rebuilds indexes or copies them between nodes. The default cleared setting has an Index Server node rebuild any newly assigned index during a rebalance. You cannot enable file-based rebalance when you have enabled Memory Optimized Index Storage. When you select this option, Couchbase Server copies the index files from one Index Server node to another during a rebalance instead of rebuilding them. See Index Rebalance Methods.
You can disable this feature from the UI or via REST API. To learn about disabling this feature via REST API, see Curl Command to Disable the File Transfer Based Rebalance. This feature is disabled by default.
Disabling this feature slows down the Rebalance operation.
XDCR Maximum Processes
The maximum number of threads used per node, to support XDCR. A greater number of threads increases parallelism, and may thereby produce enhanced XDCR performance. The default number of threads is 4.
The panel appears as follows:

Analytics Replicas
The number of replicas for analytics data. The absolute maximum number of replicas is 3. Each replica resides on an Analytics Node: a given Analytics Node can host either one replica, or the active data on which replicas are based. Thus, if a cluster contains three Analytics Nodes, the practical maximum number of replicas is 2; one node hosting the active data, and each of the other two nodes hosting a single replica.
The panel appears as follows:
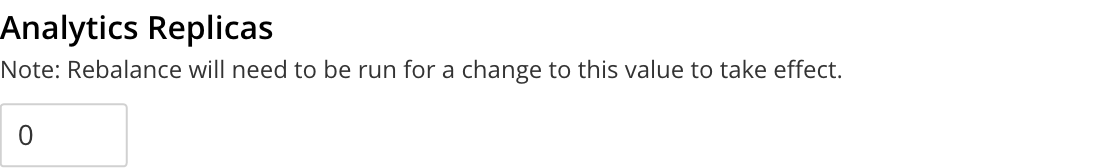
Note that if you change this setting, you must run a rebalance for the changes to take effect.
Configure General Settings with the CLI
To configure name and memory, index storage, and auto-failover via CLI, use the appropriate CLI command; as described below.
Note that no CLI support is provided for configuring query settings.
As an alternative, see Configure General Settings with the REST API, below.
Additionally, for information on URL access lists via the SQL++ CURL() function, see CURL Function.
Name and Memory Settings via CLI
Name and memory settings are established with the setting-cluster command.
/opt/couchbase/bin/couchbase-cli setting-cluster \
--cluster 10.143.192.101:8091 \
--username Administrator \
--password password \
--cluster-ramsize 256 \
--cluster-name 10.143.192.101 \
--cluster-index-ramsize 256 \
--cluster-fts-ramsize 512 \
--cluster-eventing-ramsize 256 \
--cluster-analytics-ramsize 1024This establishes the cluster-name as 10.143.192.101, the memory allocation for Data and Index Services each as 256 megabytes, and the memory allocation for each other service as zero.
If successful, the call produces the following output:
SUCCESS: Cluster settings modifiedNote that settings for an individual server may be retrieved with the server-info command, the output for which can be filtered, as appropriate, by grep:
/opt/couchbase/bin/couchbase-cli server-info \
-c 10.143.192.101 -u Administrator -p password | grep ftsThis returns the setting for ftsMemoryQuota:
"ftsMemoryQuota": 512,Index Storage Settings via CLI
Index storage can be configured with the setting-index command.
/opt/couchbase/bin/couchbase-cli setting-index \
-c 10.143.192.101:8091 \
-u Administrator \
-p password \
--index-log-level info \
--index-stable-snapshot-interval 40000 \
--index-memory-snapshot-interval 150 \
--index-storage-setting default \
--index-threads 8 \
--index-max-rollback-points 10This establishes the logging level as info, the stable snapshot interval at 40 seconds, the memory snapshot at 150 milliseconds, and the storage setting as default (which means standard, rather than memory optimized).
The number of threads to be used is established as 8, and the maximum number of rollback points to 10.
For information on the significance of these values see setting-index.
If successful, the call produces the following output:
SUCCESS: Indexer settings modifiedSoftware-Update Settings via CLI
You can enable and disable software update notifications in Couchbase Server Enterprise Edition using the setting-notification command.
/opt/couchbase/bin/couchbase-cli setting-notification \
-c 10.143.192.101 -u Administrator -p password \
--enable-notifications 1Setting value of 1 for --enable-notifications enables update-notifications. A value of 0 disables notifications.
If successful, the command produces the following output:
SUCCESS: Notification settings updated| You cannot disable software update notifications in Couchbase Server Community Edition. |
Auto-Failover Settings via CLI
Auto-failover can be configured with the setting-autofailover command.
/opt/couchbase/bin/couchbase-cli setting-autofailover \
-c 10.143.192.101:8091 \
-u Administrator \
-p password \
--enable-auto-failover 1 \
--auto-failover-timeout 120 \
--max-failovers 2This enables auto-failover, with a timeout of 120 seconds, and an event-maximum of 2.
If successful, the command returns the following output:
SUCCESS: Auto-failover settings modifiedFor a detailed description of auto-failover settings, policy, and constraints, see Automatic Failover.
Query Settings via CLI
You can set all of the cluster-level query settings, except for the CURL access control settings, using the setting-query command.
To get the current cluster-level query settings, use the --get option:
/opt/couchbase/bin/couchbase-cli setting-query \
-c 10.143.192.101:8091 \
-u Administrator \
-p password \
--getTo set cluster-level query settings, for example the log level and the maximum parallelism, use the --set option:
/opt/couchbase/bin/couchbase-cli setting-query \
-c 10.143.192.101:8091 \
-u Administrator \
-p password \
--set \
--log-level debug \
--max-parallelism 4For additional details on the cluster-level query settings, refer to Settings and Parameters.
Rebalance Settings via CLI
To obtain the cluster’s current rebalance settings by means of the CLI, use the setting-rebalance command, with the --get option:
/opt/couchbase/bin/couchbase-cli setting-rebalance \
-c 10.143.192.101 \
-u Administrator \
-p password \
--getIf successful, the command returns the current rebalance settings:
Automatic rebalance retry disabled
Retry wait time: 300
Maximum number of retries: 2To modify the current rebalance settings, use the --set option; and specify appropriate values for the --max-attempts and --wait-for flags:
/opt/couchbase/bin/couchbase-cli setting-rebalance \
-c 10.143.192.101 \
-u Administrator \
-p password \
--set \
--max-attempts 3 \
--wait-for 200If successful, the command displays the following success message:
SUCCESS: Automatic rebalance retry settings updatedFor more information, see the reference page Configure Rebalance Retries.
XDCR Process Setting via CLI
To configure the number of XDCR processes for the node, use the setting-xdcr command, with the --max-processes option:
/opt/couchbase/bin/couchbase-cli setting-xdcr \
-c 10.143.192.101 \
-u Administrator \
-p password \
--max-processes 5If successful, the command returns the following message:
SUCCESS: Global XDCR settings updatedAnalytics Settings via CLI
To obtain the current Analytics replica settings by means of the CLI, use the setting-analytics command, with the --get option:
/opt/couchbase/bin/couchbase-cli setting-analytics \
-c localhost \
-u Administrator \
-p password \
--getIf successful, the command returns the current replica settings:
numReplicas: 0To establish the number of replicas for Analytics Service data, use the setting-analytics command, with the --set and --replicas options:
/opt/couchbase/bin/couchbase-cli setting-analytics \
-c localhost \
-u Administrator \
-p password \
--set \
--replicas 3If successful, the command returns the following message:
SUCCESS: Analytics settings updatedConfigure General Settings with the REST API
Multiple REST API methods are provided to support configuration of general settings. These are described below.
Name and Memory Settings via REST
To establish name and memory settings, use the /pools/default method.
curl -v -X POST -u Administrator:password \
http://10.143.192.101:8091/pools/default \
-d clusterName=10.143.192.101 \
-d memoryQuota=256 \
-d indexMemoryQuota=256 \
-d ftsMemoryQuota=256 \
-d cbasMemoryQuota=1024 \
-d eventingMemoryQuota=512This establishes the cluster’s IP address as its name, and assigns memory-quotas to the Data, Index, Search, Analytics, and Eventing Services.
Note that when used with GET, /pools/default returns configuration-settings.
The output can be filtered, by means of a tool such as jq:
curl -s -u Administrator:password \
http://10.143.192.101:8091/pools/default | jq '.ftsMemoryQuota'If successful, this returns the value of the key ftsMemoryQuota:
256Update Notification and Statistics Settings via REST
In Couchbase Server Enterprise Edition, you can use the /setting/stats endpoint to turn off notifications about new server versions and reporting of cluster statistics back to Couchbase:
curl -v -X POST -u Administrator:password \
http://10.143.192.101:8091/settings/stats \
-d sendStats=falseYou cannot change this setting in Couchbase Server Community Edition.
The sendStats setting is always true in this edition.
See the update-notifications option in the cluster-init command line interface reference for details of what sendStats shares.
Node Availability Settings via REST
To establish node availability settings, use the /settings/autoFailover method.
curl -v -X POST -u Administrator:password \
http://10.143.192.101:8091/settings/autoFailover \
-d enabled=true \
-d timeout=120 \
-d failoverOnDataDiskIssues[enabled]=false \
-d failoverOnDataDiskIssues[timePeriod]=120 \
-d maxCount=2 \
-d failoverPreserveDurabilityMajority=trueThis enables auto-failover, with a timeout of 120 seconds, and a maximum failover-count of 2. Auto-failover is enabled in the event of suboptimal disk responsiveness, with a time-period of 120 seconds specified. Auto-failover is prohibited in cases where this might result in the loss of durably written data.
For more information on these options, see the descriptions provided above, for the UI.
Additionally, the /settings/autoReprovision method can be used; to specify that if a node containing active Ephemeral buckets becomes unavailable, its replicas on the specified number of other nodes are promoted to active status as appropriate, to avoid data-loss.
curl -v -X POST -u Administrator:password \
http://10.143.192.101:8091/settings/autoReprovision \
-d enabled=true \
-d maxNodes=1This enables auto-reprovisioning, specifying 1 as the maximum number of nodes.
Index Settings via REST
To establish index settings, use the /settings/indexes method.
# tag::gsi-settings[]
curl -v -X POST http://127.0.0.1:8091/settings/indexes \
-u Administrator:password \
-d indexerThreads=4 \
-d logLevel=verbose \
-d maxRollbackPoints=2 \
-d storageMode=plasma \
-d redistributeIndexes=false \
-d numReplica=0 \
-d enablePageBloomFilter=false
# end::gsi-settings[]
# tag::disable-ftb-rebalance[]
curl -X POST http://<host>:8091/settings/indexes -d enableShardAffinity=false -u Administrator:<password>
# end::disable-ftb-rebalance[]This establishes the storage mode for indexes as plasma.
It also establishes a verbose logging level, and a total of 4 index threads.
For detailed information on these and other settings, see the REST reference page for the method, at Set GSI Settings.
If successful, the call returns a JSON object, which provides values for all current index settings:
{
"redistributeIndexes": false,
"numReplica": 0,
"enablePageBloomFilter": false,
"enableShardAffinity": false,
"indexerThreads": 4,
"memorySnapshotInterval": 200,
"stableSnapshotInterval": 5000,
"maxRollbackPoints": 2,
"logLevel": "verbose",
"storageMode": "plasma"
}Data Settings via REST
To set the number of reader and writer threads for Couchbase Server, use the POST /pools/default/settings/memcached/global HTTP method and endpoint, as follows:
curl -v -X POST -u Administrator:password \
http://10.143.192.101:8091/pools/default/settings/memcached/global \
-d num_reader_threads=12 \
-d num_writer_threads=8This sets the number of reader threads to 12, and the number of writer threads to 8.
If successful, the call returns an object whose values confirm the settings that have been made:
{"num_reader_threads":12,"num_writer_threads":8}See Threading for an overview of reader and writer threads. Also see the REST API reference page, Setting Thread Allocations.
Query Settings via REST
To set the directory for temporary backfill data, and establish its size-limit, use the /settings/querySettings method.
curl -v -X POST -u Administrator:password \
http://localhost:8091/settings/querySettings \
-d 'queryTmpSpaceDir=/tmp' \
-d 'queryTmpSpaceSize=2048'This specifies that the directory for temporary backfill data should be /tmp; and that the maximum size should be 2048 megabytes.
If successful, this call returns a JSON document featuring all the current query-related settings, including access-control:
{
"queryTmpSpaceDir": "/tmp",
"queryTmpSpaceSize": 2048,
// ...
"queryCurlWhitelist": {
"all_access": false
}
}The document’s values indicate that the specified values for directory and size have been established; and that the current setting for access-control restricts access to all, with no exceptions.
To specify particular URLs as allowed and disallowed, use the /settings/querySettings/curlWhitelist method:
curl -v -X POST -u Administrator:password \
http://localhost:8091/settings/querySettings/curlWhitelist \
-d '{"all_access": false,
"allowed_urls": ["https://company1.com"],
"disallowed_urls": ["https://company2.com"]}'A JSON document is specified as the payload for the method.
The document’s values indicate that https://company1.com is allowed, and https://company2.com is disallowed.
If successful, the call returns a JSON document that confirms the modified settings:
{
"all_access": false,
"allowed_urls": [
"https://company1.com"
],
"disallowed_urls": [
"https://company2.com"
]
}For additional information, refer to Query Settings REST API.
Rebalance Settings via REST
By means of the REST API, both rebalance retries and maximum concurrent moves per node can be configured.
Rebalance Retries via REST
To obtain the cluster’s current settings for rebalance retries by means of the REST API, use the GET /settings/retryRebalance HTTP method and URI, as follows:
curl -X GET -u Administrator:password \
http://10.143.192.101:8091/settings/retryRebalanceIf successful, the command returns the following object:
{"enabled":true,"afterTimePeriod":200,"maxAttempts":3}This output shows that rebalance retry is enabled, with 200 seconds required to elapse before a retry is attempted, and a maximum of 3 retries possible.
To change the rebalance settings, use the POST method with the same URI, specifying appropriate values:
curl -X POST -u Administrator:password \
http://10.143.192.101:8091/settings/retryRebalance \
-d enabled=false \
-d afterTimePeriod=100 \
-d maxAttempts=2If successful, the command returns the following object:
{"enabled":false,"afterTimePeriod":100,"maxAttempts":2}This verifies that rebalance retry has been disabled, the required period between retries changed to 100 seconds, and the maximum number of retries changed to 2.
For more information on getting and setting the rebalance retry status, see Configure Rebalance Retries, Get Rebalance-Retry Status, and Cancel Rebalance Retries.
Maximum Concurrent vBucket Moves via REST
To inspect the current maximum number of concurrent vBucket moves permitted for every node, use the GET /settings/rebalance HTTP method and URI, with the rebalanceMovesPerNode parameter, as follows:
curl -v -X GET http://10.143.201.101:8091/settings/rebalance \
-u Administrator:passwordThis returns an object, confirming the current setting as being 4 (which is the default value):
{"rebalanceMovesPerNode":4}To set a new value for the parameter use the POST method with the same URI, and with the rebalanceMovesPerNode parameter.
Note that the minimum value is 1, and the maximum 64.
curl -v -X POST http://10.143.201.101:8091/settings/rebalance \
-u Administrator:password \
-d rebalanceMovesPerNode=10If successful, the call returns an object confirming the new setting:
{"rebalanceMovesPerNode":10}For more information, see the REST reference page Limiting Concurrent vBucket Moves.
XDCR Process Setting via REST
To determine how many XDCR processes are configured per node, use the GET /settings/replications HTTP method and URI, as follows.
Note that this example pipes the output to the jq program, to facilitate readability.
curl -X GET -u Administrator:password \
http://10.143.192.101:8091/settings/replications | jq '.'If successful, the command returns the following object:
{
"checkpointInterval": 600,
"compressionType": "Auto",
"desiredLatency": 50,
"docBatchSizeKb": 2048,
"failureRestartInterval": 10,
"filterBypassExpiry": false,
"filterDeletion": false,
"filterExpiration": false,
"goGC": 100,
"goMaxProcs": 4,
"logLevel": "Info",
"networkUsageLimit": 0,
"optimisticReplicationThreshold": 256,
"priority": "High",
"sourceNozzlePerNode": 2,
"statsInterval": 1000,
"targetNozzlePerNode": 2,
"workerBatchSize": 500
}The configured number of threads is the value to goMaxProcs; which is currently 4.
To change this value, use the POST method with the same URI, specifying the required number of processes as the value to the --goMaxProcs option:
curl -X POST -u Administrator:password \
http://10.143.192.101:8091/settings/replications \
-d goMaxProcs=5 | jq '.'If successful, this returns the following object:
{
"checkpointInterval": 600,
"compressionType": "Auto",
"desiredLatency": 50,
"docBatchSizeKb": 2048,
"failureRestartInterval": 10,
"filterBypassExpiry": false,
"filterDeletion": false,
"filterExpiration": false,
"goGC": 100,
"goMaxProcs": 5,
"logLevel": "Info",
"networkUsageLimit": 0,
"optimisticReplicationThreshold": 256,
"priority": "High",
"sourceNozzlePerNode": 2,
"statsInterval": 1000,
"targetNozzlePerNode": 2,
"workerBatchSize": 500
}This output indicates that the value of goMaxProcs has been appropriately incremented.
For more information, see the reference page Managing Advanced XDCR Settings.
Analytics Settings via REST
To establish the number of replicas for Analytics Service data, use the /settings/analytics endpoint.
The GET method can be used to retrieve the current setting:
curl -X GET -u Administrator:password \
http://localhost:8091/settings/analyticsIf successful, the call returns an object such as the following:
{"numReplicas":1}This indicates that the number of replicas currently configured for the Analytics Service is 1.
To change this number to 2, enter the following:
curl -X POST -u Administrator:password \
http://localhost:8091/settings/analytics \
-d numReplicas=2If successful, the call returns an object confirming the newly established number of replicas:
{"numReplicas":2}