Join a Cluster and Rebalance
An independent Couchbase Server-node can be joined to an existing cluster.
Understanding the Join Operation
Full and Cluster administrators can use the UI or REST API to join a Couchbase Server nodes to an existing cluster. On each node to be added, Couchbase Server must have been installed and started. The process of node-addition grants to the new node the settings already established for the parent cluster. (See Manage Settings for details.) The process allow services to be assigned to the new node. If the new node was previously initialized with custom disk-paths, these are retained (although if the UI is used for the join operation, these paths can be revised).
Following node-addition, rebalance is required, to make the new node and active member of the cluster.
Note that this process has a similar effect to that described in Add a Node and Rebalance. The difference is that here, the process is inverted: rather than a cluster adding a node to itself, a node is joining itself to a cluster.
Note also, however, that a node cannot join itself to a cluster if the node has already been provisioned (that is, has had Full Administrator username and password defined, and may also have had services and memory quotas defined). If the node has been provisioned, the cluster must add the node.
Node-Joining and Certificate-Management
The examples on this page assume that the default, system-generated certificates provided by Couchbase Server continue to be resident on the cluster and the node to be joined. In a production or similar context, to ensure security, only administrator-configured certificates should be used on a cluster: these should rely on a well known Certificate Authority, whose certificate is loaded as the cluster’s root certificate. (For more information, see Default Certificates and Certificate Substitution.)
In such a context, no node can be joined to the cluster until conformant administrator-configured certificates have been loaded onto it — such activities will thus need to be performed in addition to those shown by the examples on this page.
For more information, see Adding and Joining New Nodes. A complete overview of Couchbase-Server certificate-management is provided in Certificates.
Validating Node Certificates
In Couchbase Enterprise Server Version 7.2+, the node-name must be correctly identified in the node certificate as a Subject Alternative Name. If such identification is not correctly configured, failure may occur when uploading the certificate, or when attempting to add or join the node to a cluster. For information, see Node-Certificate Validation.
Note that this requirement is automatically handled by the default, system-generated certificates provided by Couchbase Server.
Examples on This Page
The examples in the subsections below show how the same uninitialized and unprovisioned node joins itself to the same existing cluster, using the UI and the REST API respectively. Node-join is not supported by the CLI.
The examples assume:
-
A one-node cluster already exists; and is named after its IP address:
10.142.181.101. It is running the Data, Query, and Index services, and has thetravel-samplebucket installed. (To access and install this, see Sample Buckets.) -
A new node has been started. This is named after its IP address:
10.142.181.102. It has not been initialized or provisioned. -
The cluster has the Full Administrator username of
Administrator, and password ofpassword. -
The cluster is protected by the default Couchbase-Server certificate-configuration.
Join a Cluster with the UI
Proceed as follows:
-
Acccess the new node’s Couchbase Web Console instance, at
10.142.181.102:8091. The welcome screen is displayed:
-
Left-click on the Join Existing Cluster button:
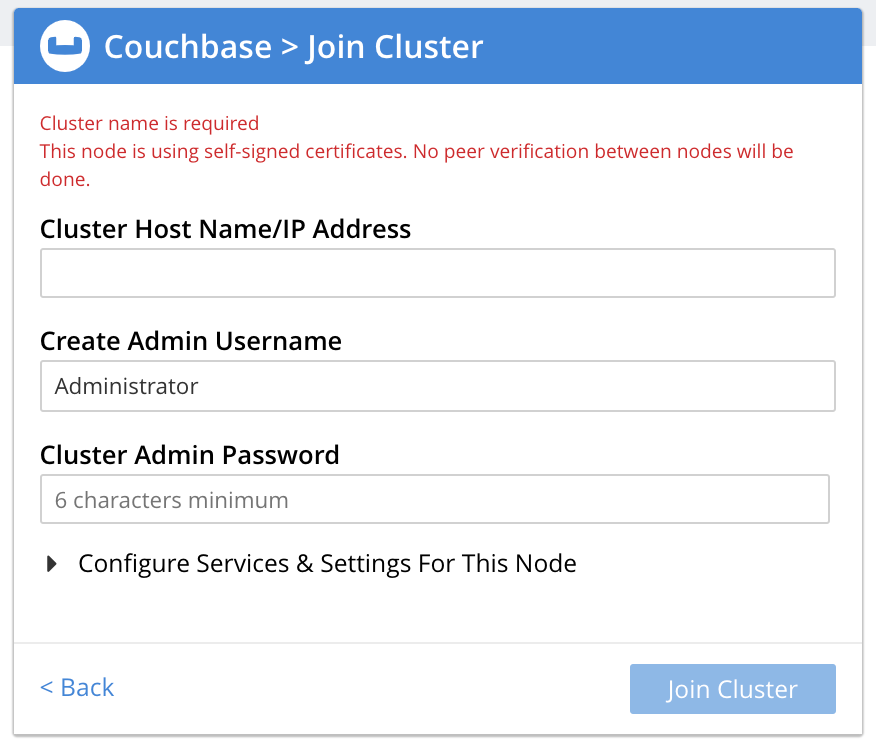
This brings up the Join Cluster dialog:
-
Left-click on the Configure Services & Setings For This Node control. The dialog expands vertically, as follows:
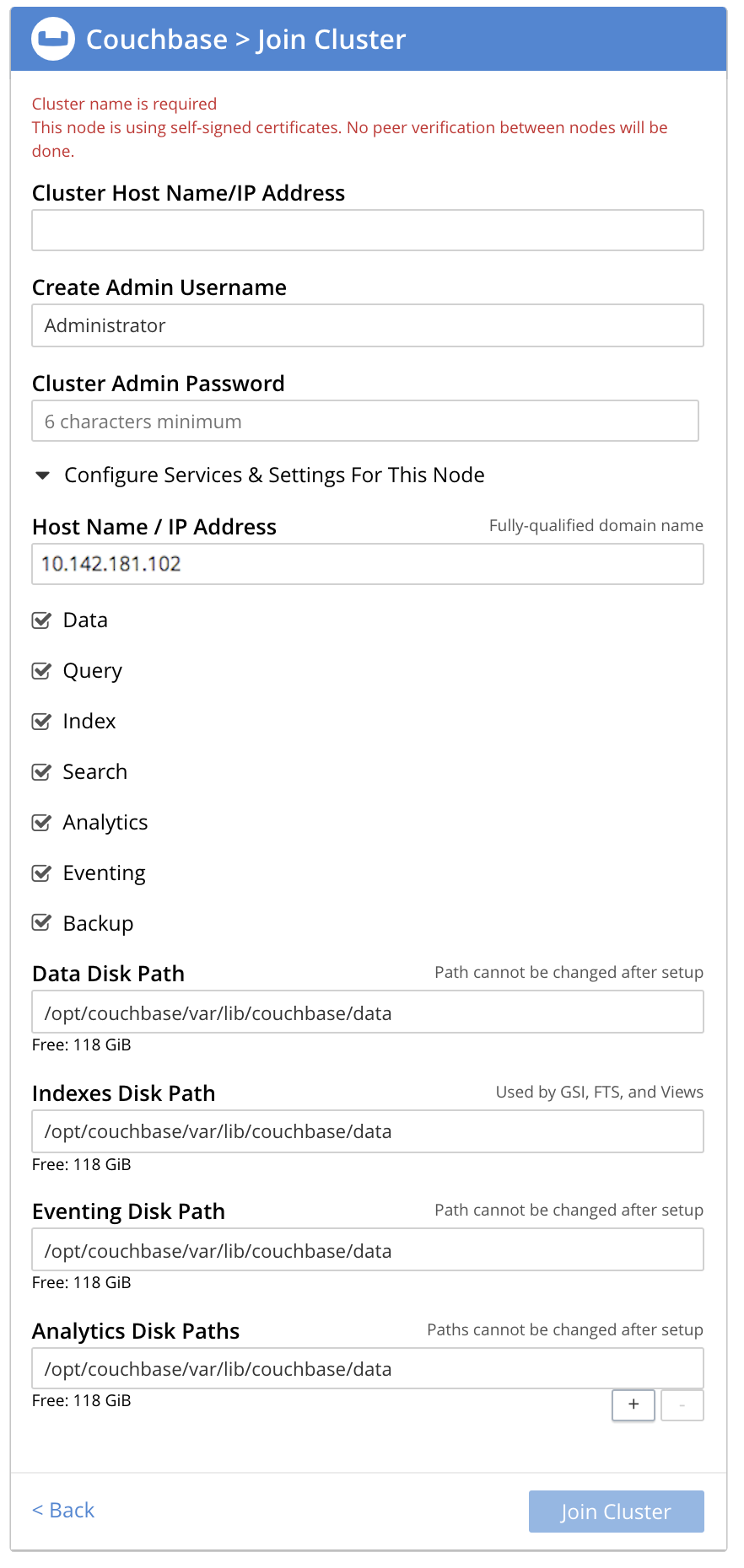
The expanded dialog allows specification of the services, the name and IP address, and the disk paths for the new node. It also requires the username and password of the Cluster Admin (although the credentials of the Full Admin for the cluster are equally implied), and the name or IP address of the cluster to be joined.
If you do not specify any services, the node joins the cluster as an arbiter node.
-
Enter the cluster’s IP address (in this case,
10.142.181.101) and password, and uncheck all Services fields except Data. Leave all other details unchanged. Then, left-click on the Join Cluster button, at the lower right.The dashboard for the cluster now appears. The following notification is provided at the lower left:

-
Access the Servers screen, by left-clicking on the Servers tab, on the left-hand navigation bar. The display is as follows:
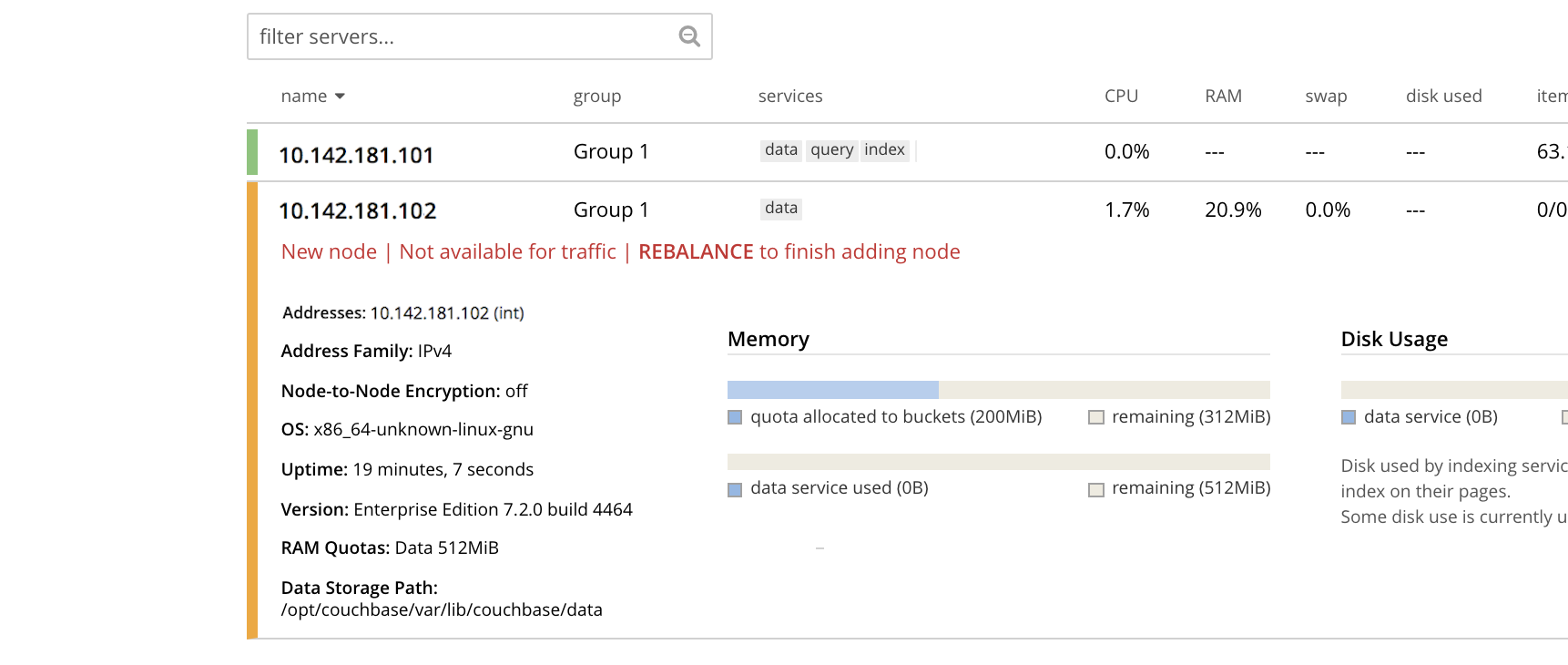
This indicates that the new node,
10.142.181.102has successfully joined the cluster. However, it is not yet taking traffic, and will be added following a rebalance. Note, at this point, the figure under the Items column for for10.142.181.101: this is63.1 K/0, which indicates that the node contains 63.1 K items in active vBuckets, and 0 items in replica vBuckets. Meanwhile, the Items figure for10.142.181.102is 0/0, indicating that no items are yet distributed onto that node in either active or replica form.To access information on buckets, vBuckets, and intra-cluster replication, see the architecture Overview.
-
To rebalance the cluster, and thereby fully add the new node, left-click on the Rebalance button, at the upper right:
Rebalance occurs. A progress dialog is shown:
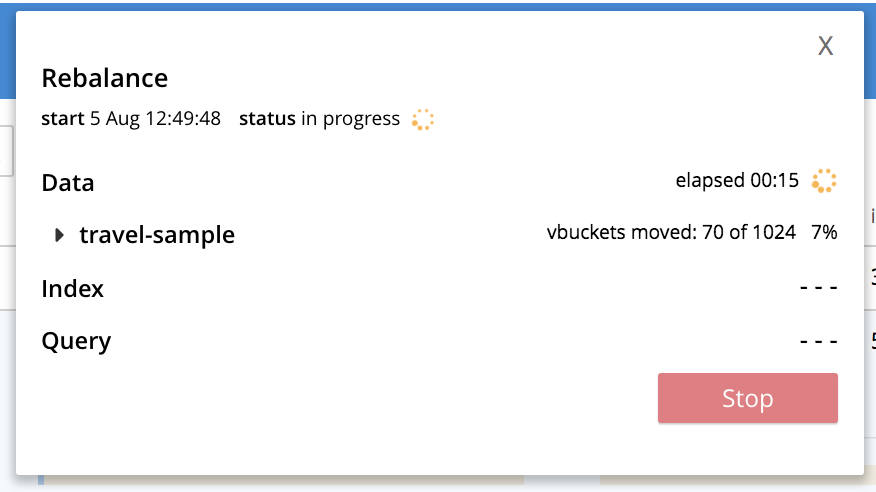
Following rebalance, the Servers display reflects the successful outcome:
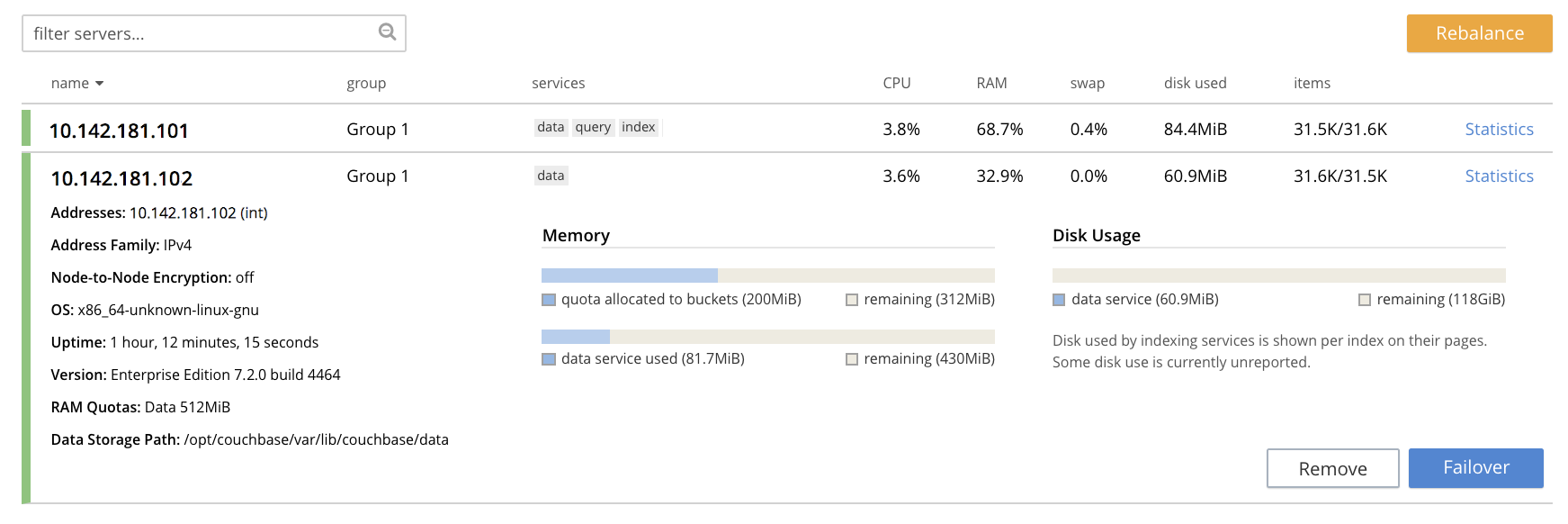
This indicates that cluster
10.142.181.101now contains two fully functioning nodes, which are10.142.181.101and10.142.181.102. (Note that the figure in the Items column for node10.142.181.101is31.5 K/31.6 K, which indicates that 31.5 K items are stored on the node in active vBuckets, and 31.6 K in replica vBuckets. The figure for10.142.181.102indicates the converse. Therefore, replication has successfully distributed the contents oftravel-sampleacross both nodes, providing a single replica vBucket for each active vBucket.)
Note that if rebalance fails, notifications are duly provided. These are described in Rebalance Failure Notification. See also the information provided on Automated Rebalance-Failure Handling, and the procedure for its set-up, described in Rebalance Settings.
Restricting the Joining of Nodes
To ensure cluster-security, in Couchbase Server Version 7.1.1+, restrictions can be placed on joining, based on the establishment of node-naming conventions. Only nodes whose names correspond to at least one of the stipulated conventions can be joined. For information, see Restrict Node-Addition.
Join a Cluster with the REST API
To join a node to a cluster with the REST API, use the /node/controller/doJoinCluster URI.
Enter the following:
curl -u Administrator:password -v -X POST \ http://10.142.181.102:8091/node/controller/doJoinCluster \ -d 'hostname=10.142.181.101&user=Administrator&password=password&services=kv'
The hostname and user(-name) and password of the Full Administrator for the cluster to be joined are specified.
The service specified to be run on the new node is kv, signifying the Data Service.
At this point, the newly joined node must be rebalanced into the cluster.
Use the /controller/rebalance URI, as follows:
curl -u Administrator:password -v -X POST \ 10.142.181.101:8091/controller/rebalance \ -d 'knownNodes=ns_1@10.142.181.101,ns_1@10.142.181.102'
Note that the knownNodes argument lists each of the nodes in the cluster.
If successful, the command returns no output.
For further information on joining a cluster with the REST API, see Joining Nodes into Clusters; on rebalancing, see Rebalancing Nodes.
Next Steps
Couchbase Server allows you to list the nodes within a cluster. See List Cluster Nodes for details.

